Upstream Authentication
Overview
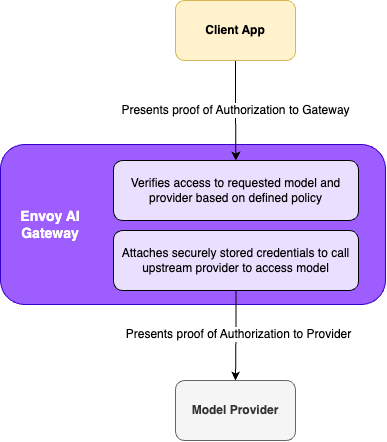
Upstream Authentication secures the connectivity between the Gateway and the LLM Providers. This layer ensures secure communication and proper access control when the Gateway interacts with various AI service providers like AWS Bedrock, Azure OpenAI, Open AI, Mistral, Gemini, and other platforms.
Why Upstream Authentication Matters
Upstream Authentication is essential for several reasons:
-
Security Layer: It provides a secure authentication mechanism between the Gateway and upstream providers, preventing credentials sprawl across teams and organizations.
-
Credential Management: It allows AI platform teams to handle the secure storage and management of credentials and use them in one place. This makes the revocation and rotation of credentials easier.
-
Compliance: It helps organizations meet security and compliance requirements by maintaining proper authentication protocols and enforcing controlled usage of AI resources.
Enterprise Security Architecture
In enterprise environments, security is implemented in multiple layers:
-
Client to Gateway Authentication
- Clients must authenticate to the Gateway using appropriate methods (API keys, OAuth, etc.) aligned with the organization's security standards.
- This ensures only authorized clients can access the Gateway's services, and the Gateway enforces the access to the upstream providers and models.
tipCheck out Envoy Gateway Security Documentation for Client to Gateway security configuration options.
-
Gateway to Upstream Authentication
- The Gateway must authenticate to upstream providers.
- This layer is managed by Upstream Authentication.
- Ensures secure communication between the Gateway and AI service providers.
Credential Management
Where the providers support short lived access credentials, the Envoy AI Gateway control plane supports automated credential management with the providers' identity system. This ensures a short-lived proof of authorization, such as an access token, is used when the request is sent to the upstream service.
For providers that support long lived access credentials, the Envoy AI Gateway control plane supports a manual credential management process. In these cases the credentials, like API keys, are stored in Kubernetes secrets and managed by the administrator.
Automated Credential Management
The Gateway integrates with each provider's identity system to ensure secure, short-lived authentication:
- AWS Bedrock: Uses OIDC integration with AWS STS to generate temporary credentials for each request
- Azure OpenAI: Leverages Entra ID (formerly Azure AD) to provide short-lived access tokens
In both cases, the Gateway automatically manages these credentials, ensuring that each request to upstream providers is sent with short-lived credentials. This approach significantly reduces the risk of credential exposure and aligns with enterprise security best practices.
Learn more about connecting to AWS Bedrock and Azure OpenAI in the provider specific documentation.
Manual Credential Management
For providers that support long lived access credentials, the Envoy AI Gateway control plane supports a manual credential management process. In these cases the credentials, like API keys, are stored in Kubernetes secrets and managed by the AI Gateway administrator. Envoy AI Gateway will use the credentials from the secret to authenticate with the upstream service, attaching them to each request by securely retrieving them from the secret and attaching them to the request.
Learn more about connecting to Open AI and adding your API key to the secret. You can use the same approach for other providers that support long lived credentials.
Conclusion
Upstream Authentication is a key component of the Envoy AI Gateway's security architecture. It ensures secure communication between the Gateway and upstream AI service providers while supporting modern authentication methods and enterprise security requirements. Leverage Envoy AI Gateway's Upstream Authentication to maintain a secure and compliant AI infrastructure in your enterprise environments.